A Homeowner’s Checklist: Identify, Prevent, and Control Common Household Bugs
Pest Control

Discovering a pest infestation can be unsettling, but with a proactive approach, you can maintain a comfortable and healthy living environment. This checklist provides essential strategies for every homeowner to identify existing problems, implement preventative measures, and effectively control common household intruders.
Few things derail home comfort faster than a sudden bug problem. Whether its ants streaming across a countertop, a cockroach sighting at night, pantry moths in cereal, or itchy bites that whisper “bed bugs,” the secret to staying pest-free is a simple loop:
- Identify the pest correctly.
- Prevent by removing food, water, and shelter.
- Control with targeted, least-risk methods.
That loop is the heart of Integrated Pest Management (IPM)—the science-backed approach endorsed by the U.S. EPA to stop pests economically while minimizing risk to people, pets, and the environment.
This checklist walks you step-by-step through how to identify household bugs, what they want from your home, and how to break their life cycles—fast.
Homeowner’s Checklist: Identify, Prevent and Control
Ants (kitchen counters, windowsills, bathrooms)
Key signs: trails; small mounds outdoors; activity peaks with weather changes.
Why they’re here: sweets/grease/water; plant honeydew; easy entry points.
What works:
Identify species, controls differ. Baits are most effective because they reach the queens; spraying foragers is short-lived. Seal entry points; maintain tight food storage; wipe trails with soapy water.
Pro tip: Place ant baits along trails (not randomly). Re-evaluate after 7–10 days; rotate active ingredients if activity persists.
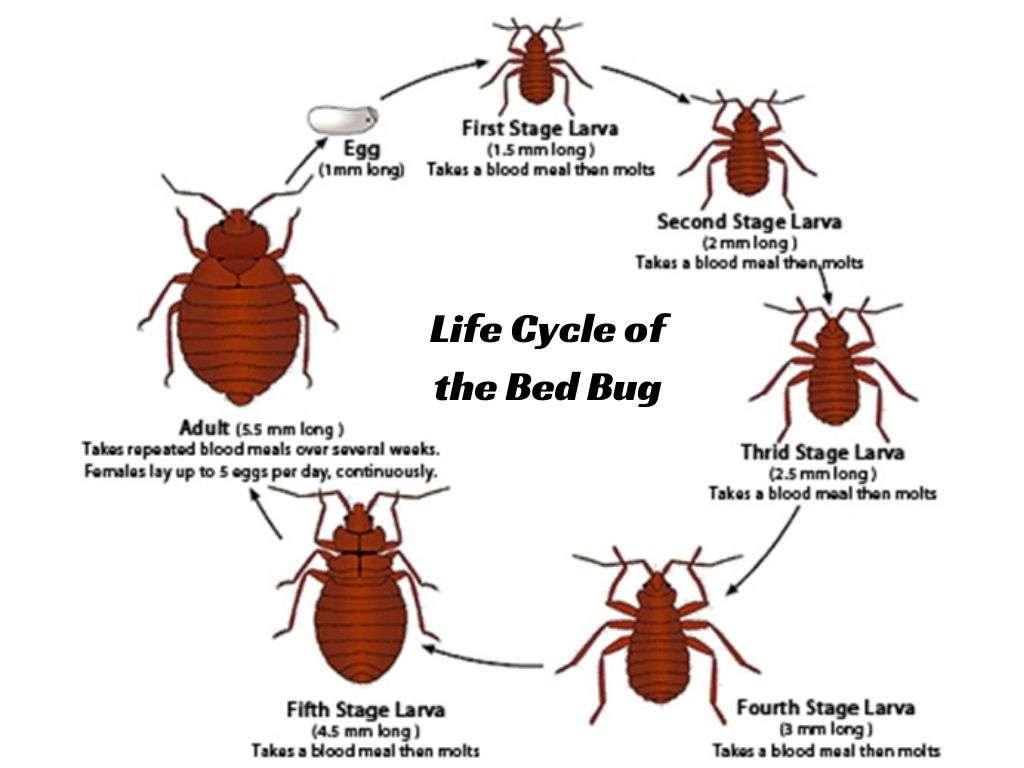
Bed Bugs (bedrooms, couches, luggage seams)
Key signs: bites in rows/clusters (not a reliable diagnostic alone), rusty spots, shed skins, eggs on mattress seams/tufts, behind headboards.
Why they’re here: hitchhikers from travel, used furniture.
What works:
Early detection saves money. Inspect seams, box spring edges, bed frame cracks; encase mattresses; launder on high heat; use interceptors under bed legs; combine non-chemical and chemical tools within an IPM plan.
Pro tip: Don’t rely on foggers. Bed bugs hide deep; targeted treatments and monitoring are critical.
Cockroaches (kitchens, bathrooms, utility rooms)
Key signs: fast movement at night, droppings like pepper, musty odor, egg cases (oothecae).
Why they’re here: water leaks, food debris, sheltered cracks.
Health note: Roaches spread bacteria and trigger asthma/allergies, especially in kids.
What works:
Sanitation + exclusion + baits. Fix leaks; vacuum crevices; remove grease/crumbs; use gel baits and growth regulators; dust wall voids where appropriate.
Pro tip: Sticky monitors (behind fridge/stove/sink) reveal hotspots so you can place baits precisely.
Silverfish & Firebrats (bathrooms, attics, closets)
Key signs: silvery, teardrop bodies; chew paper/fabrics; love humidity and warmth.
What works:
Moisture control (dehumidifiers, repair leaks), tight-lidded storage for papers/fabrics, reduce clutter; targeted baits/dusts if needed.
Pantry Moths & Stored Food Pests
Key signs: small moths at night; larvae and webbing in grains, nuts, cereal, pet food.
What works:
Discard infested items; vacuum/clean shelves and cracks; store airtight; freeze vulnerable foods to break life cycles.
Mosquito Exposure
Key signs: dusk/dawn activity; bites near doors/windows; standing water outside.
What works:
Eliminate standing water weekly (buckets, birdbaths, toys, gutters), maintain screens, use CDC-listed repellents; support local mosquito programs.
Pro tip: Water that cannot be dumped (ornamental ponds) can be treated with BTI (mosquito dunks) or kept moving with bubblers to prevent larvae. Recent how-to guides emphasize “no standing water = no nursery.”
Quick-Look ID: What’s That Bug?
Use this fast triage to narrow the culprit before you dive deeper:
- Ant lines on counters/windowsills; small mounds outdoors ants. Baiting reaches the queen; sprays on foragers don’t.
- Oval, flat, reddish-brown insects that hide in beds/sofas & feed at night bed bugs (look for rusty spots, shed skins, tiny eggs in seams).
- Fast runners, nocturnal, with droppings like coffee grounds; often in kitchens/baths cockroaches (sanitation + baits + exclusion). Also linked to asthma/allergies.
- Silvery, carrot-shaped insects in bathrooms/attics/closets silverfish/firebrats (love humidity; fix moisture, store papers/fabrics sealed).
- Moths fluttering from pantry; webby clumps in grains/nuts Indian meal moths (discard infested food; clean & store airtight; freezing helps).
- Whining bites around dusk; standing water outside mosquito exposure (drain water weekly; screens; CDC-listed repellents).
If you’re unsure, save a specimen in a clear bag/jar and note where you found it (room, material). Progressive Pest Control can confirm ID and plan next steps.
Identify the Intruders
The first step in control is identification. Different bugs require different treatment methods.
Bug Type | Common Signs of Infestation |
Ants | Visible foraging trails, small piles of sawdust (carpenter ants), or ant mounds near foundations. |
Cockroaches | Musty odor, droppings that resemble coffee grounds or black pepper, shed skins, and visible egg casings (oothecae) in dark, warm areas. |
Mosquitoes | Persistent buzzing, itchy bites on residents, and standing water sources near the home. |
Spiders | Webs in corners, isolated areas, or near light sources; often seen on window sills or in basements. |
Rodents (Mice/Rats) | Droppings, gnaw marks on food packaging or structures, nesting materials (shredded paper/fabric), or scratching noises in walls or attics. |
Preventative Measures (The Proactive Approach)
Prevention is always easier and less expensive than eradication. Most pest issues stem from access to food, water, or shelter.
1. Seal Entry Points
Pests need only a tiny gap to enter your home.
- Caulk and Seal: Inspect around windows, doors, and utility pipe entry points for cracks or crevices. Use appropriate sealant or caulk to close these gaps.
- Check Vents and Screens: Ensure all window screens are free of tears and that attic/crawl space vents are covered with intact mesh screens.
- Door Sweeps: Install or replace worn-out door sweeps on all exterior doors to eliminate gaps at the threshold.
2. Eliminate Food and Water Sources
A clean kitchen is your best defense against cockroaches and ants.
- Store Food Properly: Keep all pantry items, including cereal boxes, flour, and sugar, in airtight plastic or glass containers.
- Wipe Down Surfaces: Clean up spills immediately. Wipe counters, sweep floors, and wash dishes daily.
- Manage Garbage: Use trash cans with tight-fitting lids and take out the garbage regularly.
- Fix Leaks: Repair any leaky faucets, pipes, or running toilets to remove easily accessible water sources that attract pests like cockroaches and mosquitoes.
3. Maintain Your Yard and Exterior
Your home's perimeter is the front line of defense.
- Trim Shrubbery: Keep tree branches and shrubs trimmed away from your home’s siding and roofline. Vegetation can act as a "bridge" for ants, rodents, and other insects.
- Clear Debris: Remove leaf piles, old tires, and other yard debris where pests like to nest and hide.
- Proper Drainage: Ensure gutters are clean and direct water flow away from the foundation to prevent dampness that attracts pests.
Control and Eradication Methods
If an infestation has already taken hold, targeted control methods are necessary.
Pest Type | Control Methods |
Ants/Cockroaches | Use bait stations near entry points to target the colony/nest. Apply residual insecticides as a barrier along baseboards or entryways. |
Mosquitoes | Eliminate all sources of standing water. Use insect repellent with DEET or Picaridin when outdoors. |
Spiders | Vacuum up webs and spiders regularly. Reduce clutter in basements and garages. |
Rodents | Use snap traps placed perpendicular to walls where activity is noted. Steel wool is effective for plugging small holes as rodents cannot chew through it. |
When to Call a Professional
For severe infestations, such as established termite colonies, bed bugs, or a persistent rodent problem that DIY methods can't solve, it is highly recommended to contact a licensed pest control professional. They have access to commercial-grade treatments and expertise to safely and permanently resolve the issue.
At Progressive Pest Control, to avail our expert services contact our professional or call now at (770) 791-0055.
Conclusion
A bug-free home isn’t luck, it’s a system. When you identify correctly, prevent conditions that support pests, and control with targeted, least-risk methods, you stop infestations and keep them from returning. That’s the IPM advantage: safer, smarter, and proven.
For more information, see our pillar article, Common Household Bugs Every Homeowner Should Know and How to Identify Them, to identify common household bugs and how to identify them.
Need fast, precise help?
Contact Progressive Pest Control at (770) 791-0055 for an IPM-driven inspection and a custom treatment plan today.
FAQs
Not reliably. Sprays kill foragers you see but won’t reach the queen. Baits or nest-directed control is the effective route.

